What is enterprise search and how does it help?

Popular search engines like Google and Bing are so enmeshed in our everyday lives that have become synonymous with search in most of our minds. However, though web search and enterprise are broadly comparable, they work in quite different ways and serve distinct purposes. Enterprise search tools are for use by employees. They retrieve information from all types of data that an organization stores, including both structured data, which is found in databases, and unstructured data that takes the form of documents like PDFs and media.
The term “enterprise search” describes the software used to search for information inside a corporate organization. The technology identifies and enables the indexing, searching and display of specific content to authorized users across the enterprise.
IT industry analysts have shared that enterprise search is growing into something new. In 2017, for instance, Gartner created a new enterprise search category called “Insight Engines.” These solutions help business synthesize information interactively, or even proactively, by ingesting, organizing and analyzing data. Forrester, another prominent analyst firm, defines this new category as “Cognitive Search.”
How does enterprise search work?
Content is the raw material for enterprise search
More and more data to analyze, structure and classify
Data becomes more pervasive within a business as the organization grows. There can be a huge proliferation of product information, process information, marketing content and so forth. Individual teams create content, which then inevitably spreads across the enterprise.
Diversity of data
The information found inside large organizations tends to be highly diverse and fragmented. It’s invariably hosted on a broad range of repositories and enterprise applications. These include Content Management Systems (CMS’s), Enterprise Resource Planning solutions (ERP), Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS’s), file systems, archives, data lakes, email systems, websites, intranets and social networks as well as both private and public cloud platforms.
The data comes from a variety of sources. Structured and unstructured data are kept in different “containers.”
How enterprise search indexes, classes and ranks data
Search engine process
The enterprise search process occurs in three main phases:
- Exploration – Here, the enterprise search engine software crawls all data sources, gathering information from across the organization and its internal and external data sources.
- Indexing – After the data has been recovered, the enterprise search platform performs analysis and enrichment of the data by tracking relationships inside the data—and then storing the results so as to facilitate accurate, quick information retrieval.
- Search – On the front end, employees request for information in their native languages. The enterprise search platform then offers answers—taking the form of content and pieces of content—that appear to be the most relevant to the query. The query response also factors in the employee’s work context. Different people may get different answers that relate to their work and search histories.
Techniques like Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning are often involved in determining relevant answers to queries.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP, a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI), involves interactions between humans and computers that take the form of natural, human-like language. Its ultimate objective is to make sense of human languages in a way that is valuable to the process at hand, with the computer reading, deciphering, understanding the human language.
Machine Learning
Machine learning applies AI to give systems the ability to learn and improve from experience, automatically, without the need to be programmed explicitly. It focuses on creating computer software that can access data and then make use of it for learning purposes.
User Experience Design
User experience (UX) design is about creating products that deliver relevant, meaningful experiences to end users. It comprises the design of the entire process required to acquire and integrate the product. This includes branding, design, function and usability.
Why is enterprise search strategic in big companies?
Content without access is worthless
Enterprise search helps people in an organization find the information they need to perform their jobs. It gives them access to data extracted from inside the business, along with external data sources like document management systems, databases, paper and so forth.
Time is money: how Enterprise Search increases productivity
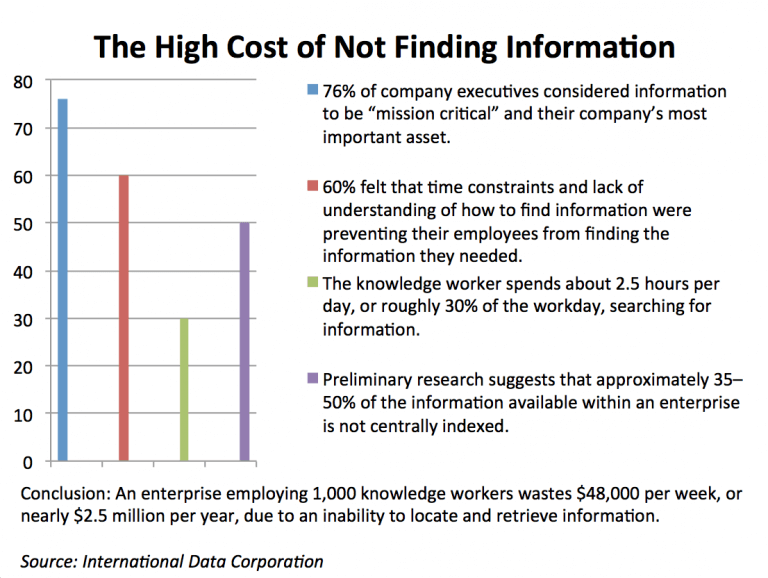
Studies reveal the cost of employees spending time finding knowledge:
- “The knowledge worker spends about 2.5 hours per day, or roughly 30% of the workday, searching for information.” – IDC
- “The research found that on average, workers in both the U.K. and U.S. spent up to 25 minutes looking for a single document in over a third of searches conducted.” – SearchYourCloud
- “The average digital worker spends an estimated 28 percent of the workweek searching e-mail and nearly 20 percent looking for internal information or tracking down colleagues who can help with specific tasks.” – McKinsey & Company
Enterprise search software reduces the time employees require to find the necessary information. As a result, it opens up work schedules for more high-value tasks. This improvement is particularly important given the current emphasis on getting optimal performance out of teams in lean, digital, agile organizations.
Enterprise Search, Insight Engine or Cognitive Search
Cognitive search, the new generation of technology for information gathering, uses AI capabilities like NLP and machine learning to ingest, analyze and query digital data content from multiple sources. Users receive results that are more relevant to their intentions. Cognitive search solutions are essential to delivering the most valuable customers and employee experiences.
Apply Enterprise Search to many Use Cases
Enterprise search engines can put to work across many different use cases in order that are intended to improve productivity:
- Digital workplace – Enabling teams to be more productive and collaborate effectively using enterprise search as part of an overall digital workplace experience.
- Customer service – Giving customer service representatives the ability to quickly and easily find the information they need to deliver excellent customer service.
- Knowledge management – Applying enterprise search to facilitate the corporate knowledge management process.
- Contact experts – Letting employees search for experts and filter results according to expertise and knowledge.
- Talent search – Matching candidates with job descriptions from a database of potential candidates.
- Intranet search – helping intranet users locate information they need from shared drives and databases.
- Insight engines – Leveraging AI to detect relationships between people, content and data as well as connections between user interests and current and past search queries.
What are the main criteria to select an enterprise search software?
Connectors
How many data connectors will an enterprise search engine need for the data sources it has to index? The best practice is to include the sources that are likely to be indexed in the future in addition to what is planned for current indexing. If a company plans to decommission a data source in a year or so, however, it may want to exclude it from the connection and indexing processes. This is particularly true if the data is going to migrated to a new source.
Privacy & Security
Data security and privacy is of paramount importance in the enterprise search process. The enterprise search platform must be configured to comply with corporate security policies, SOC2 and regulations like GDPR. Efforts must be made to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data. Critical business assets must be protected.
The following enterprise search platform characteristics and features help make sure that information and documents are only accessible to users with the right permissions:
- Adhering to international and industry-specific compliance standards
- Protecting content from malicious actors using built-in encryption in the indexing pipeline
- Customizing the process regarding IP restrictions and encryption
- Synchronizing with single sign-on (SSO) providers
- Controlling access on a per-user basis and using security filters for indexed content
- Using multilayer security across the cloud, on-premises data centers, intranets and operations
Intelligent search or Predictive AI
Predictive AI is seen as the future of enterprise search engines. With self-learning algorithms embedded in enterprise search tools, it is possible to innovate by learning from users and improving results based on their usage patterns. Furthermore, by using custom APIs that are designed to make search tools work optimally for a given audience, it is possible to deliver fine-tuned results that improve over time.
A digital workplace solution to improve productivity
The exploding data and hours of time that employees waste looking for what they need has other ramifications, as well. Without a reliable way to search through and contextualize all the structured and unstructured data that exists, insights are routinely missed, and the value of the data is lost.
Employees often need to ask colleagues for help finding the information they need, wasting additional time and resources and slowing progress. And in the end, the digital workplace that was meant to facilitate more creative, nonroutine work actually ends up producing the inverse.
An enterprise search solution can solve this information crisis. It can search and retrieve data regardless of format, type, language, and location. But more than that, it can use AI to understand the context of each piece and match it to the search intent. And the more data it is fed, the more it learns, returning better results with each query.
To the end user, it is a simple and familiar experience that delivers powerful results. For businesses overall, it’s a key building block in their digital transformation.








